How adding a Security Certificate can improve your rank on Google
Most of the time security and search engine optimization (SEO) are separate topics. When it comes to a website’s security status SEO and security cross paths.
A security certificate is used to verify the identity of a website. In the past only sites accepting credit card information needed to use an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) Certificate to verify their identity.
Recently this has changed significantly. Google is pushing security certificates in two significant ways.
Google Ranks Secure Sites Above Insecure Sites
 According to numerous sources, Google is preferring site using SSL certificates over non-secure sites in rankings. This was not a factor in the past. But, recently Google has said sites that go to trouble of setting up security certificates are more likely to have reliable and accurate content.
According to numerous sources, Google is preferring site using SSL certificates over non-secure sites in rankings. This was not a factor in the past. But, recently Google has said sites that go to trouble of setting up security certificates are more likely to have reliable and accurate content.
Moving up in rankings is one thing all webmasters are trying to do. Why not switch you site to use the HTTPS protocol along with an SSL Certificate so that everyone can see how much you care about your visitors and delivering you content in the safest environment possible.
Google Chrome Browser Marks Insecure Sites as ‘Not Secure’
The Chrome Web Browser marks sites as ‘Not Secure’ since version 68 released July 24, 2018. This was not the case in previous versions.
You can see in this in the address bar at the top of the browser.
In the latest version of Chrome (currently version 69) you will see the following for the same site.

Side by side you can see the address bar shows ‘Not Secure’ on the newer version of the browser on the right hand side of the picture.
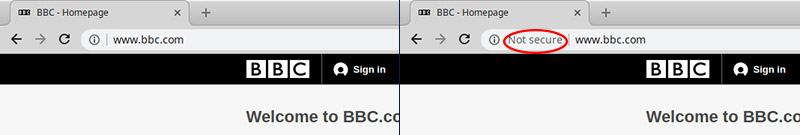
It is not the usual full page secure warning that you see when you go to a site that has an invalid SSL certificate, but it does say not secure.
This could have significant impact on user trust for websites that offer sensitive information such as medical or health advice. Or sites that offer legal or financial data.
If you would like more reassurance of this you can simply do a search on Google and note how many of the top results are secure but looking for the https:// the URL.
The Internet is constantly evolving and security is even increasing. Many blogs may have content that they find valuable or large amounts of data about their visitors.
SEO Pitfalls When Switching to SSL
If you are considering securing your website you may want to be aware of some SEO issues this can cause if you do not implement to SSL certification correctly.
Changing a page from http to https will be seen by Google spiders are creating a totally new page. You will want to be sure to use a 301 permanent redirect to force all non-secure URLS to be redirected to secure URLS. Using a 301 redirect is optimum for passing all ranking from your old pages to your ‘new’ secure pages.
Here is an example of a permanent redirect to the secure version of your site:
RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
These rules would need to added to your site’s main .htaccess file. This should only be done once your Security Certificate is properly installed. This will redirect all traffic to the secure version of your website.
Another possible issue can occur when you have subdomains and your SSL certificate doesn’t match for all subdomains. This can create the dreaded full screen security warning due to domain name mismatch. The same situation can occur with other domains you have pointed at your site try to use SSL certificate of the main domain and get a domain mismatch on the certificate.
HSTS Policy
Once you have fully tested all pages of the secure version of you website, you can consider implementing an HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) Policy. This will enforce the secure version of your website in the client browser. This is much more secure, but that means that the insecure version of your site will no longer be accessible.

